- Conscious vs. Subconscious:
The concept of the “critical faculty” refers to the mental mechanism that actively evaluates and filters incoming information through the lens of conscious thought. This critical faculty acts as a gatekeeper, assessing the validity, relevance, and credibility of information before allowing it to influence our thoughts and behaviours. In a state of trance, this filtering mechanism becomes significantly relaxed, creating a unique opportunity for the mind to bypass ordinary conscious scrutiny. As a result, individuals gain direct access to their subconscious beliefs, deep-seated patterns, and buried memories, which often shape their perceptions and reactions in everyday life. This altered state can facilitate profound insights and transformative experiences, enabling individuals to understand and reconfigure limiting beliefs that may impact their well-being.
- Neural Pathways & Habits:
Repeated suggestions play a crucial role in shaping neural pathways in the brain, much like the way repetitive use can carve a distinct rut into a gravel road. As these suggestions are reinforced over time, they create deeper and more defined grooves, transforming these patterns into what can be described as “habit highways.” These highways facilitate the efficient flow of information and behaviour, making it easier for the brain to access and execute established patterns without conscious effort. The process illustrates the brain’s remarkable ability to adapt and streamline responses to familiar stimuli, ultimately solidifying habits that influence our daily actions and decisions.
- Imaging Studies:
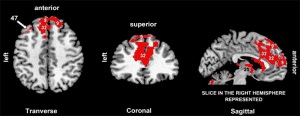
A concise summary of fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) findings reveals significant insights into brain activity. Notably, there is a marked reduction in activity within the anterior cingulate cortex, a region associated with emotional regulation and decision-making. In contrast, there is an increase in connectivity between attention networks, suggesting enhanced communication and collaboration among the brain areas responsible for focus and concentration. These findings highlight the complex interplay between different neural circuits and their roles in cognitive functions.
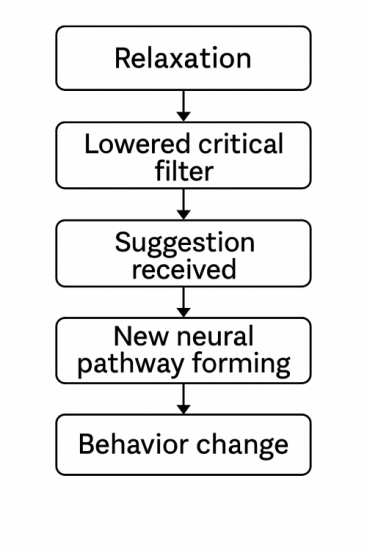
- A flowchart showing: “Relaxation → Lowered critical filter → Suggestion received → New neural pathway forming → Behaviour change.”
Understanding the Brain: Conscious vs. Subconscious
Diagram Overview
- A simple brain diagram: conscious (neocortex) vs. subconscious (limbic system).
- Neocortex (Conscious Mind):
- The “thinking cap.”
- Handles logic, reasoning, decision-making, language, and willpower.
- This is the part that tries to remember why you walked into the kitchen.
- Limbic System (Subconscious Mind):
- The “emotional engine room.”
- Governs habits, emotions, memory storage, and automatic responses.
- Also responsible for those mysterious cravings, deja-vu, and, yes, singing ‘80s pop lyrics you haven’t heard since 1987.
Quick Humour Tip
Think of your brain like an old-fashioned car:
- The neocortex is the driver, smart, alert, but easily distracted by shiny objects and interesting thoughts.
- The limbic system is the engine, powerful, emotional, and occasionally takes you on a detour (“Why did I just eat that whole cake?”).
If willpower were all you needed, the conscious mind would have us all running marathons at 6 a.m. Instead, the subconscious mind hits the snooze button and dreams about breakfast.
Why This Matters for Hypnosis
- Hypnosis helps the conscious and subconscious work together.
- In hypnosis, we quiet the “chatter” of the neocortex and give the limbic system a chance to receive new, helpful suggestions.
- That’s how real change happens, where logic meets emotion and willpower finally gets a little backup!
Bottom Line (Classic Edition)
The conscious mind is the captain; the subconscious is the crew.
For smooth sailing, it’s best if they’re both rowing in the same direction.
